Gammee2380 (talk | contribs) m (Tag: Visual edit) |
Gammee2380 (talk | contribs) m (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| Line 1,882: | Line 1,882: | ||
Figure 13 Optimum analysis of compressive strength of C-25 Concrete | Figure 13 Optimum analysis of compressive strength of C-25 Concrete | ||
| − | The optimum | + | The optimum analysis of compressive strength of concrete modified calcined MMT clay powder and KHA was produce Concrete up to 15% or proportion of B (P-B). |
'''3.13.2 Optimum mix of split tensile strength of Concrete''' | '''3.13.2 Optimum mix of split tensile strength of Concrete''' | ||
| − | + | The split tensile strength of the concrete test was conducted by 14<sup>th</sup> and 28<sup>th</sup> days. The mean targeted split tensile strength of 81.98% was fulfilled, depending on its strength 1.82(MPa) (0.82*2.22mpa = 1.82MPa). Figure, 14 is used to determine the percentage replacement in which split tensile strength of Concrete is greater than or equal to the targeted mean strength of C-25 grade concrete. | |
Table 16 the variable of split tensile strength of C-25 concrete<span id="_Toc68692742"></span> | Table 16 the variable of split tensile strength of C-25 concrete<span id="_Toc68692742"></span> | ||
Revision as of 13:41, 28 October 2021
ABSTRACT
Some environmental issues are industrial wastes and cement productions, which cause high gas emissions. Cement is vital in the global construction industry. The research goal was to find a cheaper material locally. Using OPC, calcined Montmorillonite clay powder (CMMT) and waste Khat Husk Ash (KHA) were tested as a partial replacement. Water entering the interlayer molecular spaces and adsorption, a material in expansive soil, causes Montmorillonite clay to expand more than other clays. Most of Ambo's land is expansive soil, from which samples were taken to determine Montmorillonite clay content. The average temperature required to calcine Montmorillonite clay was performed at 800 degree centgrides using a muffle furnace, ground to the fineness of 150μm, and its chemical composition was investigated. Similarly, the waste Khat husk ash was burned until the wastage of khat changes to ash. The proportions by weight are applied for the OPC modified with Calcined Montmorillonite clay powder and Waste Khat Hush Ash as follows: Proportion-A (100%: 0%: 0%);Proportion-B (85%:10%:5%); Proportion-C (75%:20%:5%);Proportion-D (65%:30%:5%); Proportion-E (55%:40%:5%) and Proportion-F (45%:50%:5%). The production of concrete for the C-25 Grade mix design was performed based on the ASTM standard specification, ERA manual, and the ACI code to evaluate the strengths and durability of concrete. These materials were calcined and then tested for strength and durability using ASTM C 618-5 to determine the chemical compounds at various temperatures. The experiments used aggregates up to 25mm in size. The results showed that when Ordinary Portland cement was partially replaced with Calcined MMT clay powder and Khat husk ash, the consistency and setting time remained within the ASTM C-191 Standard Specifications. Moreover, the compressive, flexural, and split tensile strengths gradually decreased from the control specimen as the partially replacement was increased. The optimal amount of calcined montmorillonite clay powder and Waste Khat husk ash indicated up to 15% by weight to replace OPC content in normal concrete mix production. The benefit cost analysis revealed that using Ordinary Portland cement with calcined Montmorillonite clay powder and Khat husk ash is more cost-effective than using OPC alone.
Keywords: Calcined Montmorillonite Clay; Concrete mix; Strength and durability of concrete; Expansive soil; Khat Husk Ash.
1. Introduction
The most widely used manufactured building material is concrete. These are made from natural materials and have been used as building materials for a long time. Although concrete and mortar have many advantages, their corrosion resistance is critical. Concrete durability refers to its ability to withstand various environmental conditions. Durability is the ability to meet standards of strength, stability, and serviceability over time. The choice of durable concrete components and concrete mix design is crucial (Safi, Muhammad, Tariq, Khan, Sajjad, & Muhammad, June 2019). Concrete has undergone many studies and modifications to achieve the desired properties, as long- lasting and strong concrete is always in demand. To meet this demand, blended cement concrete was developed, in which cement is partially replaced by other pozzolanic elements. Conversely, cement in concrete is increasing (Guyo, Emer, & Getachew, 2019). Some experts, however, have criticized its environmental impact. The following complaint was made regarding the manufacture of Portland cement, which emits greenhouse gases (Rehan & Nehdi, 2005). From some academics, producing one tonne of Portland cement releases approximately one tonne of CO2. It accounts for 5% of global CO2 emissions (Ahmad Hadri & Noor Faisal, 2015). Every ton of cement produced by burning fossil fuels and calcareous carbonation produces around one ton of CO2 (Ahmad Hadri & Noor Faisal, 2015). Industrial waste is the main environmental issue, and the climate is released. Blended cement has grown in popularity over time due to its low cost, environmental friendliness, and sustainability. Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) production uses more energy and pollutes the environment (Krishna, 2016). According to this researcher, gas emissions are directly proportional to cement production. As a result of rapid urbanization and infrastructure projects in Ethiopia, cement manufacturers are expanding and polluting the environment. Natural resource consumption also costs cement production. Cement versus aggregates and water in concrete production versus CO2 emissions (Guyo, Emer, & Getachew, 2019). According to ERA, black cotton is high- percentage Montmorillonite clay. The expansive soil expands as the soil moisture content increases. This paper covers the methods for reducing atmospheric CO2 and the project cost of replacing cement with calcined montmorillonite clay powder and Khat ash waste for concrete production. The production of cement requires massive amounts of raw materials, energy, and heat. The cement industry is closely linked to the state of the construction industry and thus closely monitors the overall economic situation. Cement is an energy-intensive industry that accounts for roughly 40% of total energy costs, excluding c capital and electricity costs (Sadaqat Ullah Khan, 2013).
According to (Joel, 2012), around 7% of CO2 is emitted into the environmental during cement production, which is harmful to the environmental and human future. Until now, research has focused on partial cement replacement with different materials. Partially replacing cement with pozzolans is common in advanced countries. Many modern concrete structures use admixtures and pozzolana to improve porous concrete structure and reduce CH in pozzolanic processes. Improved microstructure improves the durability and life of cement composites (Courard , Anne, & marleen, 2003). Mixes are the most common partial cement replacement for standard concrete. Despite its huge impact on the environment, solid waste is now seen daily all over the world (LOPEZ, 2009).
Cement production was severely impacted in the surrounding area, reducing gas emissions by replacing various mineral admixtures. Many studies use mineral admixtures, but none of them studied the effect of Calcined Montmorillonite (CMMT) clay powder on the hardened concrete worldwide, and specifically in Ethiopia, where its entire land mass comprised of about 33% expansive soils. In this study the partial replace of Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) with CMMT clay powder and waste of Khat husk ash that could reduce significantly CO2 emissions considering a calcination temperature up to 800oC, unlike for the production of OPC, the material is heated from 1,3000C – 1,5000C.
The study investigates the temperature activation of clay for local montmorillonite clay. The heated of montmorillonite clay as a partial replacement for cement in concrete. Used as an additional cemented pozzolanic material. In hard concrete strength and durability, the partial replacement of cement by CMMT clay powder and Khat husk ash waste. Besides, recycling the waste Khat husk in urban and rural areas would clean the local area environment. Partial substitution of OPC by calcined MMT clay powder and waste khat Husk ash can reduce the overall project cost due to abundant expansive soils mostly on the project sites. So, to educate and disseminate the suitability of CMMT clay powder as partial replacement of OPC, including KHA waste, this study hypothesized and introduced a large area of expansive soils which are found in Ambo town. Hence, this novel research study used Calcined Montmorillonite clay powder and waste Khat husk ash to produce C-25 grade concrete. The objectives of the research are: (1) To determine the chemical and physical properties of the materials ingredients for C-25 concrete production; (2) To determine and analyze the strengths and durability of concrete with Calcined Montmorillonite clay powder and waste khat husk ash; (3) To determine the effect of the different proportions of calcined MMT clay powder, OPC, and waste KHA in the concrete strengths using regression analysis; (4) To analyze the benefit cost derived from the modified materials and the normal concrete production.
2. Materials and Research Methodology
2.1 Materials Selected
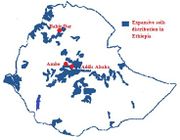
Land mass of Ambo town is composed of almost 90% black cotton soils (expansive soils). It is located of about 120 km west of Addis Ababa with a latitude and longitude of 8059'N 37051'E with an elevation of 2,101 meters above sea mean level. In the 2018 National Census, Ambo had 48,171, with 24,634 men and 23,537 women. On the other hand, Buno Bedele town is a woreda in southwest Ethiopia where an abundant Khat husk wastes collected for the experiment. This town in Oromia region is located at 8027'N 36032'E and it is between 2,012-2,162 meters above sea mean level. Buno Bedele is 426km southwest of Addis Ababa.
|
|
|
| (a) Global distribution of expansive soils | (b) Expansive soils distribution Ethiopia | (c) Ambo town (Study area) |
2.2 Criteria for selecting a source of materials
The different materials used for the study; are: coarse aggregates, sand, cement, and mineral admixtures in modified calcined montmorillonite clay powder, calcined waste khat husk and potable water. The experimental tests were assessed on the production of concrete materials partial replacement of OPC by the khat hush ash, and calcined montmorillonite clay powder collected the constituents of raw materials. Those are:
1. Coarse aggregate and fine aggregate
The coarse and fine aggregates used for the study was purchased from the road construction site Gemshu Beyene construction PLC found around Ambo town, implementing the road construction in front of the Commercial Bank of Ethiopia, Wolliso project. The maximum size of aggregate used for the experiment was 25mm, while the maximum size of sand for sieve analysis used for the study was 4.75mm.
2. Cement
The type of cement used for the experiment was Dangote Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) 42.5N Grade. It was purchased from the local market.
3. Montmorillonite clay
The montmorillonite clay was found around Ambo town, and there were different expansive soils. From those soils, the black color clay was considered due to its high content of Montmorillonite minerals. The depth of excavation 1.5m below the surface level of the soil. The Montmorillonite clay was calcined at a temperature of 8000C.
4. Khat Husk Ash
Khat trees are found everywhere in Ethiopia, but more availability of Khat waste was collected from the Buno Bedele zone for the experiment.
2.3 Sample of Laboratory test procedures
The experimental tests for the strength and durability of concrete modified with Calcined Montmorillonite (CMMT) clay powder and wastage of khat husk ash on the production of concrete C-25 Grade. The following are control mix designs to modify the normal ingredients by Calcined MMT clay powder, and Waste khat husk ash, and it was prepared six trials replacement at different percentages as shown on table 1.
Table 1 Sample proportions for the laboratory experiments
|
Sample Proportion (P) |
Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC), by weight (%) |
Calcined Montmorillonite clay powder (CMMTCP, by weight (%) |
Khat Husk Ash (KHA), by weight (%) |
Total by weight (%) |
|
P-A |
100 |
0 |
0 |
100 |
|
P-B |
85 |
10 |
5 |
100 |
|
P-C |
75 |
20 |
5 |
100 |
|
P-D |
65 |
30 |
5 |
100 |
|
P-E |
55 |
40 |
5 |
100 |
|
P-F |
45 |
50 |
5 |
100 |
The following samples were prepared and checked in Materials for quality, workability of concrete, and setting time, before the properties of hardened concrete conducted, a total of 126 different samples of mold concrete was prepared:
· For Compressive strength tests of 54 samples concrete cube samples (150mm*150mm*150mm) tested on the 7th, 14th, and 28th days.
· For split tensile tests of 36 samples, a cylinder specimen (300mm*150mm) tested on the 14th, and 28th days.
· For Flexural strength tests of 36 samples (100mm*100mm*500mm) tested on the 14th, and 28th days.
To analyze all experiments, ASTM D 422-63 and ASTM C39 standard specification of the appropriate limit of finer was selected the 0.150mm (No. 100) of sieve size was passed the Calcined Montmorillonite (CMMT) clay powder, and waste khat husk ash.
2.3.1 Sample size and sampling technique
The waste of Khat husk was taken from the Monopole site, which is located around Bunno Bedele Zone, while the Montmorillonite clays (Expansive soils) were collected around Ambo town. The presence of Montmorillonite clay minerals is highly expansive soil, was the main focus of the experiments. The experiment included an investigation of the expansiveness of the soils in determining the shrinkage limit based on ASTMD
4943-89. the equation below is used to calculate the expansiveness of the soil (ERA, 2013)
Єex = 2.4Wp–3.9ws+32.5 ---------------------------- (1) Where:
Wp = PI x (%passing #40(or0.425mm)/100 ------ (2)
Ws = Shrinkage Limit x (%passing #40)/100------ (3)
Table 2 Classifications of expansive soils according to US Bureau of Reclamation
|
Colloid content %- 1 µm |
PI (%) |
SL (%) |
Potential expansion (%) |
Degree of expansion |
|
<15 |
< 18 |
>15 |
<10 |
Low |
|
13-23 |
15-28 |
10-16 |
10-20 |
Medium |
|
20-31 |
25-41 |
7-12 |
20-30 |
High |
|
>28 |
>35 |
<11 |
>30 |
Very High |
Source: ERA Manual 2013, Special investigation
The Clay soil samples to be calcined were excavated from the different locations around Hachalu Hundesa Campus (TP1), Ambo Agricultural Research Center of EIAR (TP2), and Ambo University-Main Campus (TP3). Based on ASTM D4318-05 standard consistency methods, the Atterberg limits tests have fulfilled the sample of calcined MMT clay powder due to its soil cohesiveness. One study indicated that in manufacturing Ordinary Portland Cement required burning specimens in a kiln at a temperature 13000C – 15000C. According to (Safi, Muhammad, Tariq, Khan, Sajjad, & Muhammad, June 2019), the calcination of MMT clay powder could be performed from 1000C – 10000C; thus, above and below that, the calcined temperature was not good for the high plasticity.
In this experiment, the expansive soils (with high Montmorillonite clay minerals) samples were excavated 1.50m below the natural ground level, and the 150 μm sieve size considered to pass the calcined ingredients at the temperature of 800°C by using a muffle furnace. Similarly, the wastage of Khat husk burned at a temperature of 600°C. The ashes were carefully collected and sieving followed. The chemical compounds tested at different temperatures, the highest value obtained from the sum of the main components such as SiO2, Fe2O3, and Al2O3 more than 70% (C-618-05) are selected for the experiments.
Table 3 The physical and chemical properties of OPC, MMT clay and KHA
|
Chemical and physical composition (Wt %) |
OPC |
MMT Clay |
KHA |
ASTM C618 class N (%) |
|
Sodium oxide (Na2O) |
1.67 |
0.24 |
3.5 |
0.7 |
|
Magnesium oxide (MgO) |
0.7-4.2 |
0.78 |
3.26 |
1 |
|
Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) |
4.7-6.3 |
20.5 8 |
5.87 |
18 |
|
Silicon dioxide (SiO2) |
18.7-22.0 |
49.6 8 |
54.75 |
61 |
|
Potassium oxide (K2O) |
0.51 |
1.66 |
10.38 |
0.8 |
|
Calcium oxide (Cao) |
60.6-66.3 |
1.88 |
5.53 |
6 |
|
Titanium oxide (TiO2) |
- |
0.39 |
- |
- |
|
Ferric oxide (Fe2O3) |
1.6-4.4 |
7.84 |
2.34 |
5.2 |
|
Sulphur trioxide (SO3) |
1.8-4.6 |
0.03 |
- |
4 max |
|
(SiO2) + (Al2O3) + (Fe2O3) |
- |
78.1 |
62.96 |
70 min |
|
Loss on ignition (1 hour) |
3 |
8.69 |
6.8 |
10 max |
|
% retained # 325 mesh |
- |
11.4 |
34max | |
|
Blaine fineness (cm2g-1) |
3152 |
2571 |
34# | |
|
Specific gravity (g cm-3) |
3.11 |
2.42 |
2.14 |
- |
|
Average particle size |
20 µm |
4 to 5 µm |
1-3 µm |
- |
2.5 Data collection techniques and apparatus for testing arrangement
In this research, 126 samples prepared for all strength determinations (i.e., Compressive strength = 54 samples, Split tensile = 36 samples, Flexural strength = 36 samples) of concrete mixes based on the proportion percentage of replacement of C-25 grades of concrete. The Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) was partially replaced with Calcined montmorillonite of clay powder at 0%, 10%, 20%, 30%, 40%, 50%, and waste of husk Khat Ash at 0 %, 5%, 5%, 5%, 5% and 5% by weight and another mechanism to identify the replace by P-A, P-B, P-C, P-D, P-E, and P-F.
In addition, a control mix was produced to compare the test results with samples made by partial replacement of Calcined Montmorillonites clay powder and waste husk Khat ash. The mixed design process used for the research was based on ACI Method. The mix proportion of the basic ingredients, that is, coarse aggregate, fine aggregate, and water, were the same for the control mix and for concrete produced by partially replacing Calcined Montmorillonite clay powder and Khat husk ash except replacing the OPC by the weight. Measuring the quantities of the concrete making ingredients (coarse aggregates, sand, and water) as well as partial replacement of OPC with Calcined Montmorillonite clay powder and waste Khat husk ash was performed according to the indicated proportions by weight. To compute the volume of concrete for mix design, the volume of test specimens was calculated first.
Table 4 Materials proportion mix design of compressive strength of C-25 concrete
|
Mix Proportion |
Concrete Grade (Mpa) |
W/C |
Cement (Kg) |
MCP (Kg) |
KHA (Kg) |
Fine aggregate (Kg) |
Coarse Aggregate (Kg) |
Water(L) |
|
P-A |
25 |
0.50 |
11.32 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
24.2 |
32.75 |
5.66 |
|
P-B |
25 |
0.60 |
9.68 |
1.13 |
0.51 |
24.2 |
32.75 |
6.79 |
|
P-C |
25 |
0.62 |
8.61 |
2.26 |
0.45 |
24.2 |
32.75 |
7.02 |
|
P-D |
25 |
0.65 |
7.53 |
3.39 |
0.39 |
24.2 |
32.75 |
7.36 |
|
P-E |
25 |
0.68 |
6.45 |
4.53 |
0.34 |
24.2 |
32.75 |
7.7 |
|
P-F |
25 |
0.70 |
5.38 |
5.66 |
0.283 |
24.2 |
32.75 |
7.92 |
Material proportion for 1.62m3 of split tensile strength of concrete
Table 5 Materials proportion of mix design of split tensile strength of c-25 concrete
|
Mix Proportion |
Concrete Grade (Mpa) |
W/C |
Cement (Kg) |
MCP (Kg) |
KHA (Kg) |
Fine aggregate (Kg) |
Coarse Aggregate (Kg) |
Water(L) |
|
P-A |
25 |
0.50 |
47.4 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
214.2 |
291.1 |
23.7 |
|
P-B |
25 |
0.60 |
40.53 |
4.74 |
2.13 |
214.2 |
291.1 |
28.44 |
|
P-C |
25 |
0.62 |
36.02 |
9.48 |
1.896 |
214.2 |
291.1 |
29.39 |
|
P-D |
25 |
0.65 |
31.52 |
14.22 |
1.66 |
214.2 |
291.1 |
30.81 |
|
P-E |
25 |
0.68 |
27.02 |
18.96 |
1.422 |
214.2 |
291.1 |
32.23 |
|
P-F |
25 |
0.70 |
22.52 |
23.7 |
1.185 |
214.2 |
291.1 |
33.18 |
Material proportion for 0.18m3 of flexural strength of concrete
Table 6 Materials proportion of mix design flexural strength of C-25 concrete
|
Mix Proportion |
Concrete Grade (Mpa) |
W/C |
Cement (Kg) |
MCP (Kg) |
KHA (Kg) |
Fine aggregate (Kg) |
Coarse Aggregate (Kg) |
Water(L) |
|
P-A |
25 |
0.50 |
11.18 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
23.8 |
32.34 |
5.59 |
|
P-B |
25 |
0.60 |
9.56 |
1.12 |
0.503 |
23.8 |
32.34 |
6.71 |
|
P-C |
25 |
0.62 |
8.49 |
2.24 |
0.45 |
23.8 |
32.34 |
6.93 |
|
P-D |
25 |
0.65 |
7.44 |
3.35 |
0.39 |
23.8 |
32.34 |
7.27 |
|
P-E |
25 |
0.68 |
6.37 |
4.47 |
0.34 |
23.8 |
32.34 |
7.60 |
|
P-F |
25 |
0.70 |
5.31 |
5.59 |
0.28 |
23.8 |
32.34 |
7.83 |
2.6 Study Variable
Regression analysis is used to investigate and analyze relationships between variables. To find the effect and the relationship between dependent and independent variables, linear regression uses the equation, y = MX + c.
2.6.1 Independent variable
The value of independent variables on the "X" or horizontal axis to show in the graph X-axis direction. The X -axis in this experiment, six replacement percentages designated: P-A, P-B, P-C, P-D, P-E, and P-F (i.e., replaced OPC with calcined MMT clay powder and waste KHA). In this case, the outcome was not random. It's one or more variables (Explanatory).
2.6.2 Dependent Variable
In the regression formula is y = MX + c, where Y is the response (dependent) variable. To show the output of the resulting test, the dependent variables are placed on the "Y" axis (vertical). With the partial replacement of OPC with CMMT clay powder and waste of KHA from normal concrete production, this study's output test result shows the strength of hardened concrete to resist.
2.7 Data processing and analysis
All tests were conducted in the laboratory to obtain the desired output. All samples were tested in the laboratory according to the ASTM, ACI, and ERA Manuals for concrete specimens concerning compressive strength, flexural strength, and split tensile strength to check the durability and different material properties.
2.8 Procedures followed to conduct the research & Laboratory experiments:
1. The calcined of MMT clay powder was collected at the Hachalu Hundesa campus around the new stadium, the maximum sieve size of 150µm considered.
2. The wastage of KHA was collected from Buno Bedele Zone the maximum sieve size 150µm
3. Coarse aggregate was purchased from Gamushu Bayana general construction PLC crusher plants found around the Ambo town.
4. Dangote Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) was purchased from markets found around Total gas station in ambo town.
5. Laboratory tests for fine aggregate, coarse aggregate, and OPC with calcined MMT clay powder and waste KHA were performed at Ambo University Hacalu Hundesa, Institute of Technology Material Testing and Concrete Structure Laboratory.
I. Fine aggregate; laboratory tests conducted for fine aggregate were: sieve analysis, unit weight, specific gravity (bulk, apparent, and SSD), water absorption, moisture content, silt content, and fineness modulus.
II. Coarse Aggregate: Laboratory tests conducted for coarse aggregate were; sieve analysis, unit weight, specific gravity (bulk, apparent, and SSD), moisture content, and water absorption.
III. Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) partial replacement with Calcined MMT clay powder and waste KHA: The laboratory tested the setting time and consistency of fresh mix concrete.
OPC blended with CMMT and KHA: fine aggregate, coarse aggregate, and water were batched according to their proportions and were blended with a hand mixer. The proportions are assigned by P-A, P-B, P-C, P-D, P-E, and P-F by Weight. The mix design was conducted according to the ACI mix design manual to achieve the target strength for C-25 grade in concrete production.
· Nine concrete cube samples (15cm*15cm*15cm) were taken from each mix, and compressive strength tests were performed on the 7th, 14th, and 28th days for each proportion of partial replacement.
· Six- cylinder specimens (15cm*30cm) were taken from each concrete mix. The split tensile strength tests for the specimen were performed on the 14th and 28th days.
· Six beam specimens (10cm*10cm*50cm) were taken from each concrete mix, and a flexural strength test was conducted on the 14th and 28th days
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Properties of concrete materials
3.1.1 Consistency and setting time of paste cement with Calcined MMT clay powder and KHA
The cement used in the study is Dangote OPC 42.5N Cement Grade. Initial setting time of hydraulic cement indicated by ASTM C150 and Ethiopian standard limits of 60 minutes for one Gillmore Needles test method (ASTM C 266), and 600 minutes for two Vicats Needles test methods (ASTM C191). The paste's normal consistencies are within the ASTM C-187-86 specification ranges in all blending cases. The normal consistency of hydraulic cement was between 26% and 33% when modified with calcined montmorillonite clay powder and waste khat husk ash. The outcomes are as follows:
Table 7 Consistency and setting time of partial replacement| Proportion ratio | Consistency: water-cement ratio (%) | The setting of OPC with MMT and KHA | |
| Initial setting time Minutes | Final setting time Minutes | ||
| P-A | 28 | 58 | 372 |
| P-B | 32 | 53 | 369 |
| P-C | 33 | 49 | 360 |
| P-D | 34 | 46 | 358 |
| P-E | 36 | 40 | 350 |
| P-F | 38 | 38 | 346 |
Figure 2 Consistency of OPC modified with MMT clay powder and KHA
Depending on the water-cement ratio, there are different standards for consistency and setting time. Suppose the proportion of modified montmorillonite clay powder and khat husk ash increases; adding water reduces the mixing consistency and setting time. The ASTM and Ethiopian standards recommend a cement consistency of 26% to 33%. The pastes are mixed normally. During cement testing, the Vicat plunger penetrated 10+1 mm. In this study, different mineral admixtures have different proportion ratios to replace. P-B and P-C were chosen based on the standard specification.
3.2 Silt content in the fine aggregate
According to the Ethiopian Standard and ASTM C 117 limits, silt content does not exceed 6% (Woyesa Ararsa, Emer Tucay Quezon and Abraham Aboneh, 2018). If the fine aggregate with silt content exceeds, the limit, it must be washed or rejected the materials. In the Ethiopian case, the primary source of fine aggregate is manufactured sand which is expensive, while river sand, and most of the time, silt content is more than 6%. Therefore, the mechanisms to solve percentage silt content to minimize by washing the sand otherwise rejected. Based on their study, after washing the Ambo Sandstone, the amount of silt content was 5.8%, below 6%.
3.3 Sieve Analysis for Fine Aggregate
Fine-aggregate grading within the limits of ASTM (C33-78 and C 136) is generally satisfactory for most concretes. A test in the laboratory for the fine aggregate samples on sieve analysis was conducted on the river sand compared with the (Specifications, 2002).
Table 8 Sieve analysis of fine aggregate| Sieve Size [mm] | Weight of sieve (gm) | Weight of sieve & Retained (gm) | Weight of Retained (gm) | % of retained | Cumulative % Retained | Cumulative % Passing | Specification % Passing |
| 9.5 mm | 281.4 | 281.4 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100 | 100 |
| 4.75 mm | 303.5 | 311.05 | 7.55 | 1.51 | 1.51 | 98.49 | 95-100 |
| 2.36 mm | 304.5 | 324.45 | 19.95 | 3.99 | 5.5 | 94.5 | 80-100 |
| 1.18 mm | 278.9 | 324.75 | 45.85 | 9.17 | 14.67 | 85.33 | 50-85 |
| 0.60 mm | 271.2 | 423.35 | 152.15 | 30.43 | 45.1 | 54.9 | 25-60 |
| 0.30 mm | 257.3 | 486.75 | 229.45 | 45.89 | 90.99 | 9.01 | 5-30 |
| 0.15 mm | 288.5 | 324.95 | 36.45 | 7.29 | 98.28 | 1.72 | 0-10 |
| 0.075mm | 249.9 | 257.25 | 7.35 | 1.47 | 99.75 | 0.25 | - |
| Pan | 227.1 | 228.35 | 1.25 | 0.25 | 100 | ||
| TOTAL | 500 | 256.05 |
From the above Table 8, they can see that the sieve analysis test result shows that the cumulative percent passing is within the standard limit. The test result of each sieve number complies with the standard; hence the sand has not fulfilled the requirements as per ASTM 33 standard specification.
Figure 4 sieve analysis of fine aggregate
Other requirements of ASTM C 33 (AASTHO M 6) are: The fine aggregate must not have more than 45% retained between any two consecutive standard sieves. The fine modulus of fine aggregate (sand) is 2.56%, while according to the ASTM Standard and Ethiopian standards, there are three categories and their corresponding range. Fine sand ranges from 2.20 - 2.60, medium sand from 2.60 - 2.90, and coarse sand from 2.90 - 3.20 (specifications). Therefore, the fine modulus of the result of the experiment indicated fine sand. It is preferable for the construction industry.
Table 9 Physical properties of fine aggregate
| Description | Test Result |
| Specific gravity | 2.56 |
| Silt content (%) | 5.9 |
| Water absorption (%) | 3 |
| Moisture content (%) | 1.75 |
| Unit weight(Kg/m3) | 1545 |
3.4 Sieve Analysis for Coarse Aggregate
Coarse aggregate shall have consisted of gravel, crushed stone. The grading requirements of ASTM C 33 and C 136 (AASHTO M 80) permit a wide range of grading and various grading sizes (ERA manual 2013).
Table 10 Sieve analysis of coarse aggregate| Sieve size [mm] | Mass retained [g] | % Retained | Cumulative % Retained | Cumulative %Passing | Specification %Passing |
| 50mm | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100 | 100.0 |
| 37.5 mm | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 100 | 100 |
| 25 mm | 580.7 | 29.035 | 29.035 | 70.965 | 65-100 |
| 19.0 mm | 679.3 | 33.965 | 63 | 37 | 30-70 |
| 13.2 mm | 599 | 29.95 | 92.95 | 7.05 | 10-55 |
| 9.5 mm | 101.5 | 5.075 | 98.025 | 1.975 | 0-10 |
| 4.75 mm | 39.1 | 1.955 | 99.98 | 0.02 | 0-5 |
| Pan | 0.4 | 0.02 | |||
| TOTAL | 2000 | 382.99 |
Figure 5 The sieve analysis of coarse aggregate
Based on the test performed according to ASTM C33 and Ethiopian standards, the fineness modulus of coarse aggregate indicated 3.83. Thus, it's preferable for concrete construction.
Table 11 Physical properties of coarse aggregate with ASTM standard
| Description | Test Methods | Test Result |
| Maximum aggregate size (mm) | ASTM C 136 | 25mm |
| Specific gravity | ASTM C-127 | 2.65 |
| Apparent specific gravity | ASTM C-127 | 2.7 |
| Water absorption (%) | ASTM C-127 | 2 |
| Moisture content (%) | ASTM C-566 | 1.36 |
| Unit weight(Kg/m3) | ASTM C-29 | 1400 |
3.5 Black cotton soils (Expansive soil)
The soil samples were first air-dried and properly crushed. Atterberg’s limits and linear shrinkage tests were conducted on soil samples passing #40 (0.425mm) sieve and the other tests. According to ASTM C 618, for any material to be considered pozzolanic, its Strength Activity Index (SAI) should be at least 75% of the control mix, both for 7th and 28th days, at its 20% cement replacement level. From the Atterberg’s limits and grain size analysis tests, the natural subgrade soil of the study area of TP1, TP2, and TP3, respectively, have a Liquid limit, plastic limit, and Plasticity index more than 35% passing #200 sieve sizes. Both plastic and liquid limit are whole numbers. If either the plastic limit or liquid limit could not be determined, or if the plastic limit (PL) is equal to or greater than the liquid limit (LL), report the soil as nonplastic (NP). The plasticity index of the Montmorillonite clay powder for TP1, TP3, and TP3 is 37.05%, 25.76%, 20.07%, respectively.
Figure 6 Plastic index of expansive soil
The suitable material shall have a liquid limit not exceeding 60% and a plasticity index not exceeding 30 when determined per the requirements of AASHTO T-89 and T- 90. Unsuitable soil materials has a liquid limit exceeding 60% or a plasticity index exceeding 30% when determined according to the requirements of AASHTO T-89 and T-90. Therefore, three different selected areas were taken in these experiments: (1) around Hacalu Hundessa Campus, (2) Ambo agricultural institute of technology, and (3) Ambo university main campus. In these experiments, it was considered the clay soil with more expansiveness which contains Montmorillonite clay minerals. The samples were collected and calcined with an average temperature of 800oC. The ashes served as partial replacement for Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) blended with KHA for concrete production. Among the three locations, the highest Plasticity index of soils found at TP1 (Hachalu Hundessa Campus) with 37.05%.
These are simple and more practical methods to identify expansive soils. The indirect tests conducted include the Atterberg limits and grain size distribution, which helped to determine the activity of clay (the ratio of plasticity index (PI) to the percentage of clay fractions finer than 2µm sieve size) present in the sample and degree of expansiveness (TAGEL 2016).
According to the (MWUD, Ministry of Works and urban development of Ethiopia 2009), all greyish or brownish clays in Ethiopia with Plasticity indices (PI) greater than 25% can be identified as expansive soils. Likewise, ERA of expansive soil classification it explains that the classification or rating from low to high potential usually depends on the clay content and plasticity of the clay soils.
According to ASTM D4943-08 (ASTM 2008), the standards specification of shrinkage limit (14.3 to 41.1) %, the result of TP1 was used 14% shrinkage limit and 37.02% of Plasticity index. The Alterberg limit and shrinkage limit laboratory result was analyzed and identified more soil expansiveness in black cotton (montmorillonite clay) for the three samples collected in the TP1, TP2 and TP3. The sample was selected in TP1 or Hachalu Hundessa campus area of Montmorillonite clay is the highest among all test pits locations of soil expansiveness according to Ethiopian Standards and ASTM. Therefore the expansiveness of soil in TP1 was prepared for the concrete production; the montmorillonite clay results of the expansiveness of soil in TP1 was achieved 53.24%. Hence, the classification of expansive soils in these studies is a high classification of expansiveness soil.
MMT clay was heated in a specially designed locally manufactured electric furnace control and uniform burning. The temperature was allowed to reach the target limit before placing the clay sample in the furnace. Montmorillonite clay fulfills According to ASTM C618-05 requirements was the chemical properties the summation of Silicon dioxide(SiO2), Iron oxide(Fe2O3), and Aluminum oxide(Al2O3) is more than 70% are used as natural pozzolana for concrete production. The clay samples were put in the furnace for the required duration. MMT clay was heated at different activation temperatures. The raw materials ordinary Portland cement was burned at the temperature of 13000C to 15000C. The suggested calcination temperature was between 600°C - 800°C using a muffle furnace for an hour, according to (Safi et al. June 2019). The temperature of the Montmorillonite clay soil of TP1 (Hachalu Hundessa Campus) sample was Calcined at a temperature of 800°C. The clay was heated at duration and was kept for 3 hours. Then, the material was allowed to cool down for about 6.0 hrs before pulverizing to the desired fineness as per the methods indicated. The analysis was carried out, and the materials are passing sieve 150µm. After heating, the clay samples were then packed in PVC bags to prevent moisture and placed at the laboratory room temperature.
3.6 Properties of Fresh Concrete
3.6.1 Workability test
Workability test has conducted the result of slump cone test. The workability and consistency of the concrete mixes were measured using the slump cone test ASTM C143-89 (H., Norbert and S. 2004). According to recommended values of a slump for various types of construction as given by ACI 211.1-81, for the conducted mix design in this study, all the mixes were designed to have slumped in a range between 20mm to 80mm. The slump test results for both grades of Concrete were greater than 20mm and less than 80mm, so it is within the allowable range as per the standard. The figure below shows the slumps of the Concrete comprising modified cement with the calcined Montmorillonite clay powder and khat husk ash to replacement percentages at 35% was started. The slumps cone tests to be out of the range fixed by a targeted slump of 20mm-80mm.
Figure 7 Workability of fresh concrete
From the above Figure 4.6 the slump cone of the workability of Concrete was conducted depending on the mean target (20-80) mm, the replacement percentages were started from P-A up to P-D was acceptable for the construction industry, unless the rest is low workability of Concrete according to ACI 211.1-81.
3.6.2 Properties of hardened Concrete
There are different types of tests conducted to examine the hardened properties of Concrete by the C-25 grade production of Concrete. The tests carried out are Unit weight, compressive strength, flexural strength, and splitting tensile strength.
3.6.3 Unit weight
These tests were conducted on the 7th, 14th, and 28th days. The unit weight of modified calcined MMT clay powder and KHA volume of the cubes molds was performed (0.15cm*0.15cm*0.15cm), the weight of concrete cubes was measured just before crushing the sample. When increasing the replacement percentage of MMT clay powder and KHA with cement, the unit weight of cubic Concrete was reduced according to the observed laboratory test results.
Figure 8 Unit weight of compressive strength of concrete
3.7 Compressive strength of concrete test result of C- 25 grade
A compressive strength test was conducted at the age of 7th, 14th, and 28th days. The compressive strength tests results show in the below table 12 show that the compressive strength of concrete decreases as the percentage replacement of modified montmorillonite clay and waste of khat husk ash was increased. The results show that replacing Calcined MMT clay and KHA by 15% with cement to attain maximum compressive strength at the 7th, 14th, and 28th days compared to replacing a percentage of mineral admixtures.
Table 12 the test result of compressive strength of C-25 concrete
| Replacement percentage | Compressive strength of Concrete (Mpa) | ||
| 7th | 14th | 28th | |
| P-A | 14.70 | 19.75 | 26.86 |
| P-B | 11.46 | 14.75 | 20.20 |
| P-C | 11.09 | 13.07 | 16.86 |
| P-D | 6.25 | 8.70 | 11.24 |
| P-E | 5.28 | 7.89 | 9.38 |
| P-F | 4.74 | 7.15 | 8.20 |
Figure 9 Test results of compressive strength of C-25 concrete
The compressive strength of Concrete without montmorillonite of clay and khat husk ash was 26.86Mpa on the 28th day (P-A or 0% replacement percentages). Considering at 7th days the average compressive strength of Concrete, the different percentage replacement of MMT clay powder and KHA with cement should be achieved 77.96%, 75.44%, 42.51%, 35.92%, and 32.24% from P-B, P-C, P-D, P-E, and P-F respectively. To compare the P-A (0% replacement) at the age of 7th, the compressive strength of P-A is 14.70MPa, then P-B is 11.46MPa it was decreased by 3.24MPa depending on the P-A load resist when compare with the P - A it was preferable for the construction. P-B (15% replacement) was achieved around 77.96%. The compressive strength of concrete P-C is 11.09MPa 3.61MPa decreased it depending on the P-A (14.70MPa). Then P-C was achieved at 75.44% for a construction project.
According to ASTM C 39-05 and ACI 318-05 at 14th days, the percentage replacement of MMT clay and KHA with cement has succeeded the rate of compressive strength in terms of percent 74.68%, 66.18%, 44.10%, 39.95%, and 36.20% was collected from P-B, P-C, P-D, P-E, and P-F respectively. The compressive strength of concrete at 14th days without replacement was achieved 19.75MPa, then comparing the difference between the replacement percentages. P-B (14.75MPa or 74.68%) decreased the difference between PA- and P-B is 5MPa. Then it was succeeded at 74.68%. The 6.68MPa load decreased P-C (25% replacement) to minimize from the P-A (0% Replacement) to resist the load. Then the replacement percentage of 25% or P-C was achieved 66.18% (13.07). Similarly, at the age of 28th day, 75.20%, 62.77%, 41.85%, 34.92%, and 30.53% from the proportion of P-B, P-C, P-D, P-E, and P-F, respectively. The compressive strength of concrete at 28th days is recorded without the Calcination of MMT clay powder, and KHA was 26.86MPa (P-A 0% replacement). It has analysis and identifies the load to minimize between them. In terms of P-B, the load to resist 20.20MPa, the difference between (P-A 0% replacement) is 6.66MPa. The replacement of a percentage of (P-B 15%) was achieved 75.20%. The compressive strength of P-C is 16.86MPa, compare with P-A and P-B from 10MPa and 3.34MPa, respectively, to reduce the load resistance. In contrast, P-C was achieved 62.77%. Therefore, depending on the compressive strength of Concrete, the replacement percentage of MMT and KHA was gradually decreasing the load to resist; the highest compressive strength of this study should be 20.20MPa (P-B 15% replacement) on the 28th day. From day to day, the compressive strength increased some load to resist when the percentage of replacement was increased. According to ACI 211.1-81, the relationship between water-cement ratio and compressive strength of Concrete in terms of non-air entrained Concrete of W/C P-B or 15% replacement percentage was 0.60. The mean target average of cubic compressive strength of Concrete at 28th days was achieved 20.20MPa (75.2%).
3.8 Split tensile strength of Concrete for C-25 The split tensile strength of Concrete was conducted on the 14th and 28th days. The sample tests were prepared by the partial replacement of cement with montmorillonite clay powder and waste khat husk ash by the control mix design. The split tensile strength of concrete tests results shows that in below table 14, as the replaced percentage was increased, the split tensile strength of Concrete was gradually decreased.
Table 13 test result of split tensile strength of C- 25 concrete
| Replacement percentage | Split tensile strength of Concrete (MPa) | |||
| 14th | 28th | |||
| P-A | 2.22 | 2.60 | ||
| P-B | 1.82 | 2.32 | ||
| P-C | 1.46 | 1.72 | ||
| P-D | 0.93 | 1.16 | ||
| P-E | 0.79 | 0.93 | ||
| P-F | 0.69 | 0.84 | ||
Figure 10 Test result of split tensile strength of C-25 concrete
As per ASTM C 496, the laboratory test was conducted of split tensile strength of Concrete. The split tensile strength of Concrete should be recorded without MMT, and KHA is 2.22MPa and 2.60MPa on 14th and 28th, respectively. The sample prepared by P-B 15% partial replacement has the highest value, which is 1.82MPa and 2.32MPa on the 14th and 28th days. Likewise, the lowest value, which is 0.69MPa and 0.84 at 14th and 28th days, is attained by the sample with P-F 55% partial replacement. The sample with P-A, P-B, P-C, P-D, P-E, and P-F partial replacement shows strength to decrease by 100%, 81.98%, 65.77%, 41.89%, 35.59%, and 31.08%, respectively, at 14th days of compressive strength as shown in table 20 below. The replacement percentage of P-A, P-B, P-C, P-D, P-E, and P-F shows that the compressive strength is gradually decreased by 100%, 89.23%, 66.15%, 44.62%, 35.76%, and 32.31% on the 28th day.
The split tensile strength of Concrete for C 25 the partial replacement of modified MMT and KHA with cement from 0%, 15%, 25%, 35%, 45%, and 55%. Then the P-B (15% replacement) 1.82MPa and 2.32MPa, the difference between P-A (2.22MPa and 2.60MPa) is 0.4MPa and 0.28MPa at the 14th 28th day respectively of split tensile strength was achieved 81.98% and 89.23% respectively. The split strength of P-C was recorded 1.46MPa and 1.72MPa at 14th and 28th days, respectively. Comparing with P-A and P-B reduces the load to resist when the percentage of replacing increases, then P-A (2.22Mpa and 2.60MPa) and P-B (1.82MPa and 2.32MPa) at 14th and 28th days, respectively. The proportion of P-A and P-C was attained 0.76MPa and 0.88MPa at 14th and 28th days, respectively. P-B and P-C were replaced to minimize the load to resist between them 0.36MPa and 0.60MPa at 14th and 28th days, respectively. Therefore, P-C (25% replacement) was achieved by 65.77% and 66.15% at 14th and 28th days, respectively, to resist a load of split tensile strength for C 25 concrete.
3.9 Flexural Strength of Concrete
The flexural strength of Concrete in this test the concrete beam is using by the two-point of loading to apply the flexural of Concrete. The partial replacement of modified calcination MMT clay powder and KHA with cement resists the load. The test results showed when the partial replacement percentage increase, the flexural strength of Concrete for C-25 Concrete was gradually decreasing as the table 14 shows.
Table 14 the test result of Flexural strength of C-25 concrete| Replacement percentages | Flexural strength concrete (MPa) | |||
| 14th | 28th | |||
| P-A | 2.2365 | 3.14 | ||
| P-B | 1.47 | 1.87 | ||
| P-C | 0.99 | 1.31 | ||
| P-D | 0.78 | 0.896 | ||
| P-E | 0.61 | 0.7095 | ||
| P-F | 0.44 | 0.525 | ||
Figure 11 The flexural strength of C-25 concrete
The flexural strength of Concrete was replaced proportion of P-A (2.24MPa and 3.14MPa), P-B (1.47MPa and 1.87), P-C (0.99MPa and 1.31MPa), P-D (0.78MPa and 0.896MPa), P-E (0.61MPa and 0.71MPA), and P-F (0.44MPa and 0.53MPa) at the 14th and 28th days respectively. It gradually decreased the flexural strength of Concrete. The above partial replacement proportion P-B (15% replace) was the highest strength compared with the other replacement percentages. Then the replacement of P-B was resisted load 1.47MPa and 1.87MPa at 14th and 28th days, respectively. It was more preferable than the rest can be produced for C-25 grade concrete production. In this study, it's found that the 14th and 28th days of flexural strength of Concrete containing MMT clay powder and waste of KHA with OPC particles that decrease differ from the other, which is as follows:
- When the calcined of MMT clay and waste of KHA in Concrete is P-B (15% replace), the loss of flexural strength is 34.48% and 40.59%.
- When the calcined of MMT clay and waste of KHA in Concrete is P-C (25% Replace), the loss of flexural strength is 55.64% and 58.35%.
- When the calcined of MMT clay and waste of KHA in Concrete is P-D (35% Replace), the loss of flexural strength is 65.07% and 71.48%.
- When the calcined of MMT clay and waste of KHA in Concrete is P-E (45% replace), the loss of flexural strength is 72.92% and 77.42%.
- When the calcined of MMT clay and waste of KHA in Concrete is P-F (55% replace), the loss of flexural strength is 80.51% and 83.29%.
- The flexural strength of Concrete was produced less than 15% (P-B) of partial replacement of cement with MMT clay powder and Waste of KHA. Thus, the proportion of P-B was used for the construction industry 65.52% and 59.41% on 14th and 28th days, respectively. It can be produced the Concrete of C-25 grade production.
3.10 Durability Test
The effect of Montmorillonite clay and waste khat husk ash on the durability of Concrete was investigated by using the Dry –wet strength, concrete shrinkage properties, etc. According to IS 456-2000, "a durable concrete is the one that performs satisfactorily in the working environment during its anticipated exposure during service." Durability can be understood in many ways. It is defined as the time duration until Concrete in a hardened state can withstand the weathering effects satisfactorily. The Concrete durability depends on its resistance to the ingress of aggressive agents through the pores. This property is affected by the water-cement ratio to a large extent. Good concrete should be durable in a hardened state (SAMREEN KHAN May- 2018). The compressive strength of Concrete for C 25 concrete has gradually increased for each day, then the calcination MMT clay powder and KHA with the cement of durability is to resist. As more CH is consumed during the pozzolanic reaction of calcined clay to form additional CSH gel, thus reducing CH content durability of hydrated cement is improved (Safi et al. June 2019).
3.11 Effect of dry and wet exposure strength
The compressive strength of concrete specimens decreased due to weather conditions. The compressive strength of concrete P-B was more preferable for the construction industry concerning these test results. The strength of P-B was reduced due to the weather condition of Concrete by 0.26% to this exposure. Test results show that by increasing the percentage of replacing calcined MMT clay and KHA content, the durability resistance to wet and dry seemed to decrease compared to the control samples.
Figure 12 The dry condition of compressive strength of C-25 concrete
The partial replace of P-A, P-B, P-C, P-D, P-E, and P-F the strength for C 25 concrete composed of 23.58MPa, 17.67MPa, 14.28MPa, 7.59MPa, 6.53MPa, and 5.71MPa respectively at 28th days. The strength of modified replacements was gradually decreased when the percentage of partial replacement was increased. The compressive strength for C 25 concrete of wet- dry of a sample at 28th days decreases the load to resist comparing with the normal Concrete. The percentage of compressive strength for P-B at 28th days is 75.20%, and the wet-dry strength is 74.94%. The difference between is 0.26% to reduce load resist on partial replacement of P-B (15%). Therefore the dry exposure strength of Concrete is minimized then to modify the materials' proportion in dry and wet. It needs some chemical admixtures because of setting time and consistency of Concrete due to increment or decrement of weather condition of the concrete structure. The partial replacement of cement with calcination of montmorillonite clay powder and waste khat husk ash was more W/C; when increasing the replace percentage, the water-cement ratio also increases. Therefore, the compressive strength of Concrete is less strength, so the durability of wet-dry concrete strength was low.
3.12 Shrinkage of Concrete
Durability of concrete was minimized due to the impact of concrete shrinkage. The compressive strength was evaluated by tests performed on cubic specimens (150mm*150mm*150mm) at the ages of 7th, 14th, and 28th days. The shrinkage (dry) of each mixture was measured as per the AS 1012.13 Standard. The specimens were removed from molds 24 hours after casting and then cured underwater until the 7th day when the initial length was recorded. The samples were left for drying in the laboratory air (23oC), and length change was recorded on the 28th day. Concrete shrinkage, the partial replacement of montmorillonite clay powder, and waste khat husk ash with cement change the volume of Concrete as per the cubic dimension.
3.13 Determining the optimum analysis of MMT and KHA with OPC
3.13.1 Optimum mix compressive strength of Concrete
The compressive test was utilized to examine the samples of normal Concrete produced by the partial replacement of OPC with calcined of MMT clay powder and waste KHA. The contents of percentages replace were P-A (100%, 0%, 0%), P-B (85%, 10%, 5%), P-C (75%, 20%, 5%) P-D, (65%, 30%, 5%) P-E, (55%, 40%, 5%) and P-F, (45%, 50%, 5%) at the 0%, 20%, 40% and 60% with interval of partially replacement to show the optimum regression analysis. To determine the optimum at the 28th day of compressive strength of Concrete for P-B is 75.20% of the targeted mean strength of cubes Concrete after 28th days. It implies that the compressive strength of concrete at 28th days is greater than 20.20MPa (0.75*26.86MPa = 20.20Mpa). The compressive strength regression analysis was assigned by the independent variables depending on the proportion percentage
Table 15 Regression analysis of compressive strength of C-25 concrete
| Proportion | Independent variables of % proportion | Compressive strength @ 7th Dependent Variables | Compressive strength @ 14th Dependent Variables | Compressive strength @ 28th Dependent Variables |
| P-A | 0 | 14.70 | 19.75 | 26.86 |
| P-B | 10 | 11.46 | 14.75 | 20.20 |
| P-C | 20 | 11.09 | 13.07 | 16.86 |
| P-D | 30 | 6.25 | 8.70 | 11.24 |
| P-E | 40 | 5.28 | 7.89 | 9.38 |
| P-F | 50 | 4.74 | 7.15 | 8.20 |
Figure 13 Optimum analysis of compressive strength of C-25 Concrete
The optimum analysis of compressive strength of concrete modified calcined MMT clay powder and KHA was produce Concrete up to 15% or proportion of B (P-B).
3.13.2 Optimum mix of split tensile strength of Concrete
The split tensile strength of the concrete test was conducted by 14th and 28th days. The mean targeted split tensile strength of 81.98% was fulfilled, depending on its strength 1.82(MPa) (0.82*2.22mpa = 1.82MPa). Figure, 14 is used to determine the percentage replacement in which split tensile strength of Concrete is greater than or equal to the targeted mean strength of C-25 grade concrete.
Table 16 the variable of split tensile strength of C-25 concrete
| Proportion | Independent variables of % proportion | Split tensile strength @ 14th dependent Variables | Split tensile strength @ 28th dependent Variables |
| P-A | 0 | 2.22 | 2.60 |
| P-B | 10 | 1.82 | 2.32 |
| P-C | 20 | 1.46 | 1.72 |
| P-D | 30 | 0.93 | 1.16 |
| P-E | 40 | 0.79 | 0.93 |
| P-F | 50 | 0.69 | 0.84 |
Figure 14 The average of optimum analysis of split tensile strength of C-25 concrete with dosage of OPC with MMT clay and KHA
Up to 15%, partially replacing OPC with MMT and KHA, the split tensile strength of Concrete resist the load of 1.82MPa and 2.32MPa by 14th and 28th days, respectively. Thus the proportion of P-B (15%) was preferable for normal concrete production.
3.13.3 Optimum control mix of flexural strength of Concrete.
The partial replacement of the optimum mix of flexural Concrete was conducted by 14th and 28th days of C-25 concrete production. The mean target of flexural Concrete was reached 59.41% by 28th days of the proportion of P-B (15%). Then by 28th day, the flexural strength of Concrete is greater than 1.87MPa (i.e., 0.5941 *3.14MPa = 1.87MPa).
Table 17 Average variables of flexural strength of result of C-25 concrete
| Proportion | Independent variables of % proportion | Flexural strength @ 14th dependent Variables | Flexural strength @ 28th dependent Variables |
| P-A | 0 | 2.24 | 3.14 |
| P-B | 10 | 1.47 | 1.87 |
| P-C | 20 | 0.99 | 1.31 |
| P-D | 30 | 0.78 | 0.90 |
| P-E | 40 | 0.61 | 0.71 |
| P-F | 50 | 0.44 | 0.53 |
Figure 15 average variables of optimum analysis flexural strength results of C-25 concrete
It implies that the flexural strength of Concrete which produce normal Concrete up to 15% (P-B) was achieved the optimum mix 1.47MPa and 1.87MPa by 14th and 28th days, respectively. Generally, the optimum mix by 28th day of compressive, split tensile and flexural strength of Concrete was reached 20.20MPa, 2.32MPa, and 1.87MPa, respectively. Then up to 15% (P-B) of partial replacement of OPC with MMT and KHA can produce the normal concrete.
3.14 The environmental impact of Calcined MMT clay powder and waste KHA with OPC
OPC production uses more energy and pollutes the environment by emitting carbon dioxide. They overlooked the clay's thermal activation. This study investigates the activation of montmorillonite clay in Ambo town at various temperatures. The use of Calcined MMT clay and KHA waste in concrete as a partial replacement for OPC will improve its properties. This study evaluates the effects of heated MMT clay and KHA on the mechanical strength of concrete specimens in extreme curing environments; and compares the durability of concrete when OPC is replaced with Calcined montmorillonite clay powder and waste khat husk ash at various replacement levels. To reduce the amount of gas released into the atmosphere, OPC was replaced by calcined MMT clay powder and KHA wastage. Khat husk waste is scattered throughout the city. Thus, wastage of Khat reduced urban aesthetics, then collect wastage of husk khat to prepare for partial replacement of OPC. Montmorillonite clay has a high plasticity. So it's not suitable for construction because it requires another soil for compaction to reduce plasticity in the site area. Then OPC was used to partially replace calcined MMT clay powder because OPC has higher plasticity than MMT clay powder. Generally, replacing calcined MMT clay powder and KHA with OPC reduced gas emissions.
3.15 The cost Comparison of OPC and with calcined MMT clay powder and waste KHA and OPC only
The comparison cost analysis of OPC and calcined of MMT clay and KHA wastage are identified in terms of raw materials. In this study work, the cost breakdown and economic analysis was worked out as the cost of OPC, MMT clay, KHA, sand, aggregate, and water are used for the production of plain concrete depends on its user point location; to give insight for cost benefits, the average cost without admixtures or OPC only and the partial replacement of OPC with calcined of MMT clay and wastage of KHA, sand, aggregate, and water to produce plain concrete and labour cost for the production of plain concrete production is presented below.
3.15.1 Mix design of plain concrete production cost analysis of OPC only
The mix design of control mix of plan concrete for C-15 ratio 1:2:4. The information required:
- C-15 = 1:2:4
- Dry base analysis = 1.54m3
- Unit weights;- cement = 1450kg/m3, coarse aggregate = 1400kg/m3 and fine aggregate = 1545kg/m3
- Volume of mold = (0.15*0.15*0.15)m3 = 0.003375m3
- Total compressive mold = 54*0.003375m3 = 0.18225m3
- To analyze for the C- 15 plain concrete of compressive strength of 1m3 concrete.
- 2. The mix design of split tensile strength for C-25 plain concrete.
- 3. Mix design of flexural strength of concrete for C-25 plain concrete.
Volume mould of flexural strength = (0.10*0.10*0.50) m3 = 0.005m3
The raw materials requirement of plain concrete for mix design of C-25 grade ratio production of concrete. Those raw materials are OPC and MMT clay and KHA, sand, coarse aggregate, and water.
- Total volume of cement = (0.040+0.042+0.039) m3 = 0.1217m3.
- Weight of cement = 0.1217m3*1450kg/m3 = 176.465kg
- The amount of OPC currently was purchased in the market 650.00 ETB for 100kg weight
- * Total cost of OPC without MMT clay and KHA = 176.465kg*650ETB = 1147.023ETB
- * Total volume of fine aggregate = (0.0802+0.084+0.0792) m3 = 0.2434m3
For 16m3 of river sand was purchased from the market 10,000ETB, then for this study 0.2434m3 of sand to need for the plain concrete. The amount of sand was purchased from the market = (0.2434m3*10,000ETB)/16m3 = 152.125ETB.
Total volume of coarse aggregate = (0.1604+0.17+0.1584) m3 = 0.489m3
For 16m3 of coarse aggregate was purchased from the market 18,000ETB, then for this study they need 0.489m3 of coarse aggregate. Thus the amount of coarse aggregate was purchased from the market = (0.489m3*18,000ETB)/16m3 = 550.125ETB. The total amount of raw materials for plain concrete are 550.125+152.125+1147.023 = 1849.273 ETB.
- 1. Labor cost
The cost analysis of labor cost was classified by skilled and unskilled
- 400ETB per day (skilled) = 400.00 ETB.
- 100ETB per day (unskilled) = 100.00 ETB
- Total = 500 ETB per day
- 2. Transport cost
The transportation cost of raw materials for the plain concrete such as: -
- For the OPC was paid 100ETB
- Fine aggregate and coarse aggregate were paid for transport 300ETB.
The total amount of plain concrete of raw materials, Labour cost, and transportation cost of OPC, fine aggregate, and coarse aggregate are =(1849.273+500+400)ETB = 2749.273ETB.
3.15.2 Mix design of plain concrete of cost analysis of OPC partial replacement with Calcined of MMT clay powder and wastage of KHA
The comparison cost analysis of partial replacement of OPC with the calcined of MMT clay powder and wastage of KHA. The cost comparison of constituent's materials was to identify in terms of OPC, but on the sand and coarse aggregate has equal. There are different proportions of partial replacement of OPC with Calcined MMT clay powder and wastage KHA.
- The total volume of OPC is 0.086275m3. then weight = 0.086275m3*1450kg/m3 = 125.098kg. For the 100kg weight of ordinary Portland cement was purchased from the market 650.00 ETB. The amount of OPC was purchased 125.098kg for this study by the 813.137 ETB.
- The total volume of Calcined MMT clay powder is 0.03045m3. The amount of montmorillonite clay powder was collected without any payment locally available, and when excavated, the expansive soil was paid 100 ETB for the daily labor.
- The total volume of wastage of KHA is 0.005075m3. The wastage of Khat was collected from where, in this study, without any payment, the wastage of husk Khat was collected. Therefore the total amount OPC+MMT+KHA = 813.137+0+0= 913.137 ETB was purchased. The amount of fine and coarse aggregates indicated 152.125ETB and 550.125ETB, respectively. The total amount of plain concrete are 813.137+152.125+550.15 = 1515.412ETB
- 1. Labor cost
The cost analysis of labor cost was classified by skilled and unskilled
- 400ETB per day (skilled) = 400.00 ETB.
- 100ETB per day (unskilled) = 100.00 ETB
- Total = 500.00 ETB per day
- 2. Transport cost
The transportation cost of raw materials for the plain concrete such as:
- For the OPC was paid 100 ETB without admixtures, but the weight of OPC is 125.098kg, then the amount OPC is (125.098kg*100ETB)/200ETB = 62.55ETB to paid for the transport and for KHA was collected from Bedele zone was paid 50ETB and montmorillonite was collect without pay.
- Fine aggregate and coarse aggregate were paid for transport 300ETB.
The total amount of plain concrete raw materials cost, labor, and transportation cost of partial replacement of OPC with calcined MMT clay and wastage KHA, fine aggregate, and coarse aggregate are 1515.412ETB +500ETB+412.55ETB = 2427.962ETB. Generally, the cost comparison without admixtures of OPC was release for the plain concrete are 2749.273ETB. In contrast, the partial replacement of OPC and calcined MMT clay powder and wastage of KHA were depicted with 2427.962ETB. Thus the partial replacement of admixtures is a cheaper cost when compared with admixtures. Therefore, the partial replacement of OPC by calcined of MMT clay and wastage KHA are economical to use for plain concrete, indicating a significant reduction of the total project cost for the construction industry.
4. Conclusion
The expansiveness of soil was determined using the highest plasticity index clay used to partially replace Ordinary Portland Cement when calcined at the required temperature. This study used three samples: TP1, TP2, and TP3. The TP1 result of plastic index is 37.05 percent. Expansiveness soil of Tp1 is 54.24% or a high range. This study discovered that the highest expansiveness of clay has a good pozzolanic, a chemical compound found in Ordinary Portland Cement. However, partial replacement of calcined Montmorillonite clay powder and khat husk ash with cement reduced setting time. The control mix's Calcined Montmorillonite Clay Powder and Khat Husk Ash initial and final setting times range from 38 to 372 minutes. The blended paste initial setting and final setting time decreased with partial replacement. In accordance with ASTM C191 standard P-D, P-E, and P-F is out of range due to the partial replacement. Using calcined Montmorillonite clay powder and waste khat husk ash as an OPC modifier reduced the setting time of mixed concrete. In such cases it needs accelerator of concrete admixtures:
The workability of concrete containing the modifier Calcined Montmorillonite clay powder and waste of khat husk ash gradually decrease, as the partial replacement content was increase as follows P-A (35mm), P-B (28mm), P-C (25mm), P-D (20mm), P-E (15mm) and P-F (12mm) of the partial replacement. There are some slump cones found out of the targeted slump (20mm-80mm) for C 25 grade concrete depend on ASTM C143-89 or ACI 211.1-81, the replace percentage of P- D, P-E, and P-F slump cone was out of limit. Therefore, the concrete is not workable for the construction industry at a replacement percentage higher than 35% P-D (partial replacement) of Calcined Montmorillonite clay powder modifier and wastage of khat husk ash for OPC.
As the partial replacement percentage increase, the hardened concrete slowly decreases. The result tests of compressive, split, and flexural strength of concrete on the proportion of P-B (85%, 10%, 5% replacement percentage) can resist loads as follows (20.20MPa and 75.2%), (2.32MPa and 89.23%), and (1.87MPa and 59.41%) by 28th days respectively. Therefore, the proportion of P-B has achieved the compressive, split tensile and flexural strength of concrete for the construction industry compared to the P-A (100%, 0%, and 0% partial replacement). Based on the laboratory test results and analyses of the hardened concrete at the 28th days as follows: - compressive, split tensile and flexural strength of Concrete was achieved 18.424MPa (15% replacement), 2.02MPa (15% replace), and 1.59MPa (15% replacement), respectively. Therefore the compressive, flexural and split tensile strength of concrete with varying percent amount of Calcined of MMT clay and Wastage of KHA as partial replacement of OPC, the optimum amount of MMT and KHA for normal concrete strength is 15%
The durability of compressive strength of concrete cubes prepared with thermally activated TP1 (Hancalu Hundessa campus) Montmorillonite clay and waste khat husk ash as SCM to cement provide blend for durable construction material. The clay was firstly heated/calcined at 8000C, and the wastage of Khat husk was burned up to changes to ash. Thus, it was replaced with ordinary Portland cement by different percentages of partial replacement to cast compressive strength of concrete cubes.
The control and MMT clay powder and KHA modified cubes were cured in normal curing water. The durability of concrete was achieved depending on the compressive strength unless the factors of durability in this study minimize in the case of shrinkage of concrete and dry-wet of concrete; as the test results, the compressive strength of concrete for each proportion is gradually increasing daily the strength of concrete. Thus durability is resisted load depending on the duration of concrete was increasing as per as the compressive strength of concrete. The concrete weight is gradually decreasing, and the volume of concrete is also reduced, then the factors of carbonation shrinkage do not affect the concrete. So, it has the durability of concrete achieved by partial replacement of cement with MMT clay and KHA on the life service of concrete. Generally, from the test result was conducted, the study is concluded that the Calcined of montmorillonite clay powder and waste of khat husk ash can replace with cement up to P-B (15% replace) or P-B (85%, 10%, and 5%) by the weight of normal concrete.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate Ambo University Hachalu Hundessa, Institute of Technology, and for all the individuals who assisted them in the conduct of this novel research work.
Disclosure statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
References
- A. H., & N. A. (2015). The implanation of waste concrete ash as partial replacement of cement materials in concrete. Australian journal of basic applied sciences .
- B. D. D. H. J. and S. p. , "partile size effect on the strength of rice husk ash blended gap graded protland cement concrete cement and concrete composite," pp. 357-366, 2005.
- C. l., A. D., & m. s. (2003). Durability of ortars modifed with metakaolin cement and concrete research.
- C-618-05, A. (n.d.).
- D. T. e. a. "Use of waste materials in concrete," a review journal of science and technology, pp. 499-522, 2018.
- G. K., E. T., & G. K. (2019). Calcined termite hill clay powders partial replacement of cement in the production of C 25 grade concrete. American journal of civil engineering and Architecture, 128-134.
- G. K. and G. R. d. s. , "assesement of optimal level of replacemnt for strength and permability properties of concrete construction and building materials," pp. 75-83, 2008.
- H. T., N. D., & S. A. (2004). Effect of Supplementary Cementitious Materials On the compressive strength and Durability of short term cured concrete. Cleveland state university enganged scholarship @CSU, Civil and Environmental Engineering faculty.
- Joel, M. (2012). A review of partial replacement of cement with some agro waste. Nigerian journal of technology.
- Krishna, N. K. (2016). Study on concrete with partial replacement of cement by rice husk ash. IOP Science.
- LOPEZ, R. F. (2009). Calcined Clayey Soils as a Potential Replacement for.
- N. A. "Properties of concrete fifth edition," Pearson education Ltd , 2013.
- P. Sidney Mindess, Concrete construction engineering, conistuent of concrete materials, London: United state of america, 2008.
- R. R., & N. M. (2005). Carbondioxide emissions and climate change, policy implications for the cement industry. Environmental science and policy, 105-114.
- S. U., M. Y., T. A., K. S., S. W., & M. N. (June 2019). Durability of Mortars Modified with Calcined Montmorillonite clay.
|
16. S. H. "mineralogical study of the pozzolanic properties of calcined clays," Arenberg doctoral school, faculty of science, pp. 9-15, April,2017. |
|
S. H. K. B. K. and A. V. , Design and control of concrete mixtures, london: Fourtenth edition, portland cement association , 2003. |
S. U. K. M. F. N. and &. T. Ayub, "Effects of different mineral admixtures on the properties of fresh concrete," the scientific world journal , February 2014.
Sadaqat Ullah Khan, M. F. (2013). Effects of Different Mineral Admixtures on the properties of fresh concrete.
SAMREEN KHAN. (May- 2018). STUDY OF DURABILITY OF CONCRETE. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), 248-249.
specification, E. t. (2002). standard specification of building and road materials . Finfine : ERA.
specifications, E. s. (n.d.).
Specifications, S. (2002).
T. M. (2016). Application of Marble Dust to Improve the Engineering Properties of expansive soil to be used as road bedding material . Addis Abeba University , 11.
W. A., Emer Tucay Quezon, & A. A. (2018). Suitability of Ambo Sandstone Fine Aggregate as as alternative river sand replacement in normal concrete production. American Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture, 140-146.
| [1] | S. U. R. M. Y. T. A. K. S. S. W. K. and M. N. , "Durability of Mortars Modified with Calcined Montmorillonite clay," June 2019. |
| [2] | G. K. D. E. T. Q. and G. K. , "Calcined termite hill clay powderas partial replacement of cement in the production of C-25 Grade Concrete," American Journal of civil Engineering and Architecture, vol.7,no.3, pp. 128-134, 2019. |
| [3] | R. R. and N. M. , "Carbon dioxide emissions and climate change, policy implications for the cement industry,," Environmental science and policy, pp. 105-114, 2005. |
| [4] | A. H. H. and N. F. A. , "the Implanatation of Waste concrete Ash as partial cement replacement materials in concrete," Australian Journal of basic and applied sciences. AJBAS-0007, 2015. |
| [5] | A. W. E. T. Q. and M. B. , "effect of varying dosage replacement of cement content by animal bone powder in normal concrete mix production," American Journal of civil Egineering and Architecture vol.6,no.4, pp. 133-139, 2018. |
| [6] | M. J. "A REVIEW OF PARTIAL REPLACEMENT OF CEMENT WITH SOME AGRO WASTE," NIGERIAN JOURNAL OF TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 29 NO 2, JUNE 2010, p. 12, June 2010. |
| [7] | C. L. A. D. M. S. and X. W. , "Durability of Mortars Modified with Metakaolin Cement and concrete research," pp. 1473-1479, September 2003. |
| [8] | "ERA Manual," 2013. |
| [9] | W. A. E. T. Q. and A. A. , "Suitability of Ambo Sandstone Fine Aggregate as as alternative river sand replacement in normal concrete production," American Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture, pp. 140-146, 2018. |
| [10] | E. T. S. specification, "standard specification of building and road materials," Finfine , ERA, 2002, p. 176. |
| [11] | T. M. "Application of Marble Dust to Improve the Engineering Properties of expansive soil to be used as road bedding material," Addis Abeba University , p. 11, 2016. |
| [12] | MWUD, "Ministry of works and urban development of Ethiopia," Ministry of Urban , 2009. |
| [13] | H. T. N. D. and S. A. , "Effect of Supplementary Cementitious Materials On the compressive strength and Durability of short term cured concrete," Cleveland state university enganged scholarship @CSU, Civil and Environmental Engineering faculty, 2004. |
| [14] | S. K. "STUDY OF DURABILITY OF CONCRETE," International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), pp. 248-249, May- 2018. |
Document information
Published on 05/11/21
Submitted on 17/08/21
Licence: CC BY-NC-SA license
Share this document
Keywords
claim authorship
Are you one of the authors of this document?











