(Created page with "== Abstract == In an attempt to cover the needs and requirements of consumers, packaging without good recyclability is sometimes introduced in the market. This is more eviden...") |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == | + | <span id="OLE_LINK6"></span><span id="_GoBack"></span> |
| + | ==1 Introduction== | ||
| − | + | Polyethylene terephtalate (PET) is a highly recycable material which is mainly used in packaging sector and, due to current legislation [<span id='cite-1'></span>[[#1|1]]], a whole logistic has been developed and implemented in order to allow and facilitate the recycling of PET wastes. | |
| − | == | + | {| style="width: 100%;margin: 1em auto 0.1em auto;border-collapse: collapse;" |
| − | < | + | |- |
| + | | style="text-align: center;width: 32%;"|[[Image:Roig_et_al_2018a-image5.png|162px]] | ||
| + | | style="text-align: center;width: 40%;"|[[Image:Roig_et_al_2018a-image6.png|216px]] | ||
| + | | style="text-align: center;width: 26%;"|[[Image:Roig_et_al_2018a-image7.png|126px]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="center" style="width: auto; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;"> | ||
| + | <span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">'''Figure 1.'''</span>'' ''<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">Application examples where PET material can be used.</span></div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | PET is a potential recyclable material that can provide a high quality recycled material. Current recycling of PET is mainly focused on monolayer bottles of PET with a white-blue color. This material has excellent prospect in packaging sector (bottles and films) [<span id='cite-2'></span>[[#2|2]]] as recycled material after different operations as separation, classification and cleaning. Other applications with less added value are carpets, concrete, elements for isolation and automotive parts for filtering and drainage, in bitumen mixtures and concrete, and roads stabilization (levelled). | ||
| + | |||
| + | However, packaging development to fulfil consumers’ needs promote in some occasions the introduction of market products with poor recyclability, for this it is increasingly common the presence of PET waste which come from multilayer packaging and with different colors (figure 1). | ||
| + | |||
| + | When discussing a multilayer PET packaging, it is referring to a packaging mainly made by PET, but it presents other materials like PA, EVOH or PE, what initially provided improved properties to the packaging, for example, a barrier effect that provide a better food conservation, but implies a handicap to the recyclability. | ||
| + | |||
| + | When PET bale arrive to recycling installation has time-by-time more quantity of these wastes. These new waste materials produce problems when they arrive to recycler, resulting in low quality products or even rejected products, which are delivered to landfill. This implies an important environmental loss (mainly loss of resources and production of CO<sub>2</sub> emissions) and economic loss. For this reason, recycling and waste manager companies are interesting in looking for alternatives that allow obtaining a viable solution for this kind of wastes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Nowadays, in Europe 700.000 Tons of PET trays with these characteristics are consumed every year (Source: Plastics Recyclers Europe). | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the PET material recycling, three main recycling types can be identified: Biologic or organic recycling, mechanical recycling and chemical recycling. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* Biologic recycling is not applied in PET waste, because this is not a biodegradable material. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* Mechanical recycling of PET is the most common, and this implies separation, grounding, cleaning/drying and homogenization in order to obtain a recycled material, mainly as flakes to be used in different applications. The mixture of materials with different nature with recycled PET has also been studied and a substantial decrease in the final material quality has been detected. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* Chemical recycling or depolymerization of PET consists in a glycolysis of polyester (breaking chemical bonds in the carbon chain of PET) by the use of different reactive with an excess of water (hydrolysis), alcohols (alcoholysis), glycols (glycolysis), amines (aminolysis) and ammonium (ammoniolysis) [<span id='cite-3'></span>[[#3|3]]-<span id='cite-4'></span>[[#4|4]]]. As a result, different substances and/or products with added value for the chemical industry can be obtained. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span id='OLE_LINK41'></span>Glycolisis, a type of alcoholysis, is the most suitable for the development of unsaturated polyester, vinylester, epoxy, alkyl resin and polyurethanes. This reaction consists in the breaking of ester bonds by glycols, producing olygomers or olygoesters diol/polyol with terminal hydroxyl groups. The olygoesters coming from PET glycolysis are “renewable” chemical reactives for the production of resins previously mentioned. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Substances and products obtained are recycled materials, from the environmental point of view (contributing to sustainable development and providing eco-innovated products), although from technical point of view they have same properties than initial materials, in contrast to traditional mechanical recycling in which a decreasing in properties could be observed in different degrees. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span id='OLE_LINK1'></span><span id='OLE_LINK2'></span>These factors have recently promoted the growing interest in the options to use PET wastes for the production of products as unsaturated polyester resins, alkyl resin, polyurethane foams and polymer concrete. In this context, RESIPET project “Development of New Thermosetting Resins from Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Waste” is being developed by BARPIMO Company and AIMPLAS- Plastics Technology Centre. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==2 Development== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span id='OLE_LINK30'></span><span id='OLE_LINK31'></span><span id='OLE_LINK9'></span><span id='OLE_LINK10'></span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==='''2.1''' Introduction=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span id='OLE_LINK19'></span>The main goal of RESIPET Project is the industrial development of thermoset resins (alkyl resins and unsaturated polyester), through raw materials coming from chemical recycling of multilayer or color wastes from Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) at a competitive cost and low environmental impact. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Project benefits and the developed products are relevant as follows: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* Reduction of environmental impact of alkyl and unsaturated polyester resins (less carbon footprint). | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* Replace this kind of waste PET removal with material recycling (chemical recycling), following waste hierarchy and obtaining an environmental improvement. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* Competitive cost of new developed resin (lower than conventional thermoset resins). | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* Use of separable layers of multilayer packaging. Recycling of polypropylene or polyethylene from this packaging. | ||
| + | |||
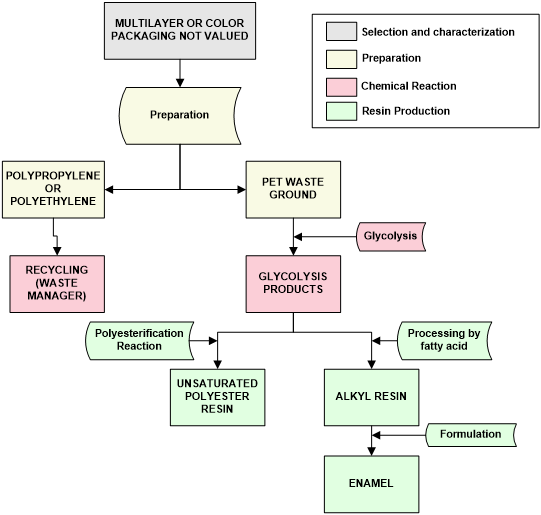
| + | The project structure is divided in four steps as it is detailed as figure 2: i) selection and characterization of PET wastes, ii) preparation of PET waste, iii) chemical reaction, iv) resin production | ||
| + | [[File:Roig_et_al_2018a-image8.png|centre|541x541px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span id='OLE_LINK3'></span><span id='OLE_LINK4'></span><span id='OLE_LINK37'></span><span id='OLE_LINK38'></span><span id='OLE_LINK26'></span><div id="OLE_LINK27" class="center" style="width: auto; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;"> | ||
| + | <span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">'''Figure 2.''' Project structure to industrial development of thermoset resins (alkyl resins and unsaturated polyester) by using PET waste.</span></div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span id='OLE_LINK39'></span><span id='OLE_LINK40'></span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==='''2.2''' Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) waste selection and preparation=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Search and selection of PET waste was carried out taking into account the following characteristics: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* They are currently not recycled (they can be a problem for PET recyclers). | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* Good accessibility, according to: a critical volume, homogeneous, competitive price | ||
| + | |||
| + | Taking these premises into account, the following waste has been evaluated from different sources: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* Fresh pizza packaging waste | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* Frozen pizza packaging waste | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* Slurry packaging waste | ||
| + | [[File:Roig_et_al_2018a-image9.png|centre|373x373px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | :1) b) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span id='OLE_LINK44'></span><div id="OLE_LINK45" class="center" style="width: auto; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;"> | ||
| + | <span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">'''Figure 3.''' Pizza packaging PET waste (a) and PET wastes ground (b)</span></div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==='''2.3''' Chemical recycling and resin production=== | ||
| + | |||
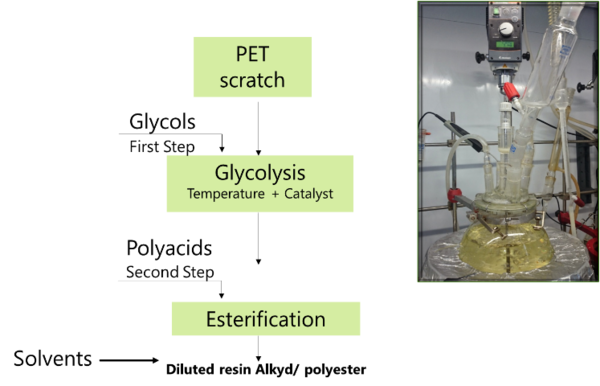
| + | PET wastes selected and conditioned have been subjected to the chemical recycling process according to scheme detailed in figure 4, obtaining a new poliol (OligoPET). These will be the starting recycled reagents for the synthesis of alkyd resins and enamels, as well as for the production of unsaturated polyester resins. | ||
| + | [[File:Roig_et_al_2018a-image10.png|centre|600x600px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="center" style="width: auto; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;"> | ||
| + | <span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">'''Figure 4.''' Process to produce Alkyd And for Unsaturated Polyesters from PET scratch</span></div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The virgin and recycled unsaturated polyester obtained by glycolysis have been characterized by different tests: viscosity, gel time, Persoz hardness, density, non-volatile content, acid number … | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="center" style="width: auto; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;"> | ||
| + | {| style="width: 87%;border-collapse: collapse;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | colspan='3' style="border-bottom: 2pt solid black;text-align: center;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">'''Table 1.''' Characterization of virgin and recycled unsaturated polyester resins</span> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="border-top: 2pt solid black;border-bottom: 1pt solid black;text-align: right;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">Resin</span> | ||
| + | | style="border-top: 2pt solid black;border-bottom: 1pt solid black;text-align: right;vertical-align: top;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">Virgin</span> | ||
| + | | style="border-top: 2pt solid black;border-bottom: 1pt solid black;text-align: right;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">Recycled </span> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="border-top: 1pt solid black;text-align: right;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">Viscositty</span> | ||
| + | | style="border-top: 1pt solid black;text-align: right;vertical-align: top;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">320 cps</span> | ||
| + | | style="border-top: 1pt solid black;text-align: right;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">345 cps</span> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="text-align: right;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">Gel time</span> | ||
| + | | style="text-align: right;vertical-align: top;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">7 minutes</span> | ||
| + | | style="text-align: right;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">8 minutes</span> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="text-align: right;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">Persoz Hardness</span> | ||
| + | | style="text-align: right;vertical-align: top;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">240</span> | ||
| + | | style="text-align: right;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">262</span> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="text-align: right;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">Density</span> | ||
| + | | style="text-align: right;vertical-align: top;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">1.14 g/ml</span> | ||
| + | | style="text-align: right;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">1.14 g/ml</span> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="text-align: right;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">Nonvolatile content</span> | ||
| + | | style="text-align: right;vertical-align: top;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">65.38 %</span> | ||
| + | | style="text-align: right;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">66.16 %</span> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="border-bottom: 2pt solid black;text-align: right;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">Acid index (mg KOH/g resin)</span> | ||
| + | | style="border-bottom: 2pt solid black;text-align: right;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">19.65</span> | ||
| + | | style="border-bottom: 2pt solid black;text-align: right;"|<span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">18.48</span> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==3 Results== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Results of the project are detailed as follows: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span id='OLE_LINK52'></span> | ||
| + | :* A new poliol (OligoPET), from chemical recycling of PET waste | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* Unsaturated polyester resin formulated by the replacement of some of polyacids and polyols by the new OligoPET. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* Alkyl resin has been formulated with the same principle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* The results of the characterization carried out show similar results to the unsaturated polyester resin from the PET wastes and to a standard resin: | ||
| + | |||
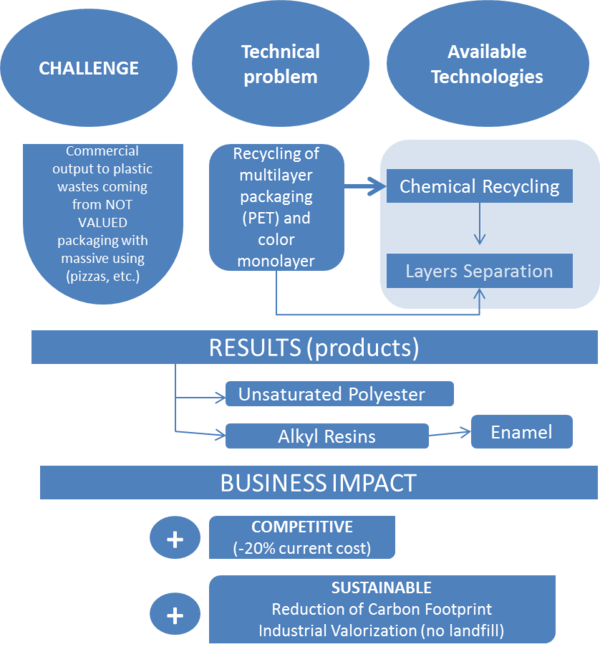
| + | Figure 5 shows an approach of the project and its involvements and results in terms of products and economic viability of the process. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="center" style="width: auto; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;"> | ||
| + | [[Image:Roig_et_al_2018a-image11.png|600px]] </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="center" style="width: auto; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto;"> | ||
| + | <span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">'''Figura 5.''' Approach of RESIPET project and its envolments.</span></div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==4 Conclusions== | ||
| + | |||
| + | As conclusions, it can be established that: | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* The implementation of technologies of preparation and chemical recycling of PET wastes coming from multilayer or color packaging are feasible. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* Alkyl and unsaturated polyester resins from not valued PET wastes (multilayer or colour packaging) can be obtained by chemical recycling. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :* Thermoset resins with low environmental impact and at competitive cost can be developed | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Acknowledgments== | ||
| + | |||
| + | This work has been co-funded by Competitivity and Economy Ministry in “Retos-Colaboracion” National Program of Research, Development and Innovation oriented to Societal Challenges RTC-2015-3855-5 and FEDER Funds. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Referencias== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div id="1"></div> | ||
| + | [[#cite-1|[1]]] <span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">Directiva 94/62/CE del Parlamento Europeo y del Consejo, de 20 de diciembre de 1994, relativa a los envases y sus residuos. DO L 365 de 31.12.1994</span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div id="2"></div> | ||
| + | [[#cite-2|2]] <span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">Mohamadi, M. et al. “Synthese und Charakterisierung von BHETA basierten neuen Polyurethanen”. ''Mat-WissU Werkstofftech, '' '''41''' (8):682-88 (2010)</span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div id="3"></div> | ||
| + | [[#cite-3|3]] <span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">Spychaj T. “Chemical Recycling of PET: Methods and Products”. En: FAKIROV S. ''“Handbook of Thermoplastic Polyesters: Homopolymers, Copolymers, Blends, and Composites”.'' Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, FRG. doi: 10.1002/3527601961.ch27, 2005: 1252-1290</span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div id="4"></div> | ||
| + | [[#cite-4|4]] <span style="text-align: center; font-size: 75%;">Shamsi R. et al. “Synthesis and characterization of novel polyurethanes based on aminolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate) wastes, and evaluation of their thermal and mechanical properties”. ''Polym Int'' '''58''':22–30 (2009)</span> | ||
Latest revision as of 20:16, 13 October 2022
1 Introduction
Polyethylene terephtalate (PET) is a highly recycable material which is mainly used in packaging sector and, due to current legislation [1], a whole logistic has been developed and implemented in order to allow and facilitate the recycling of PET wastes.

|

|

|
PET is a potential recyclable material that can provide a high quality recycled material. Current recycling of PET is mainly focused on monolayer bottles of PET with a white-blue color. This material has excellent prospect in packaging sector (bottles and films) [2] as recycled material after different operations as separation, classification and cleaning. Other applications with less added value are carpets, concrete, elements for isolation and automotive parts for filtering and drainage, in bitumen mixtures and concrete, and roads stabilization (levelled).
However, packaging development to fulfil consumers’ needs promote in some occasions the introduction of market products with poor recyclability, for this it is increasingly common the presence of PET waste which come from multilayer packaging and with different colors (figure 1).
When discussing a multilayer PET packaging, it is referring to a packaging mainly made by PET, but it presents other materials like PA, EVOH or PE, what initially provided improved properties to the packaging, for example, a barrier effect that provide a better food conservation, but implies a handicap to the recyclability.
When PET bale arrive to recycling installation has time-by-time more quantity of these wastes. These new waste materials produce problems when they arrive to recycler, resulting in low quality products or even rejected products, which are delivered to landfill. This implies an important environmental loss (mainly loss of resources and production of CO2 emissions) and economic loss. For this reason, recycling and waste manager companies are interesting in looking for alternatives that allow obtaining a viable solution for this kind of wastes.
Nowadays, in Europe 700.000 Tons of PET trays with these characteristics are consumed every year (Source: Plastics Recyclers Europe).
In the PET material recycling, three main recycling types can be identified: Biologic or organic recycling, mechanical recycling and chemical recycling.
- Biologic recycling is not applied in PET waste, because this is not a biodegradable material.
- Mechanical recycling of PET is the most common, and this implies separation, grounding, cleaning/drying and homogenization in order to obtain a recycled material, mainly as flakes to be used in different applications. The mixture of materials with different nature with recycled PET has also been studied and a substantial decrease in the final material quality has been detected.
- Chemical recycling or depolymerization of PET consists in a glycolysis of polyester (breaking chemical bonds in the carbon chain of PET) by the use of different reactive with an excess of water (hydrolysis), alcohols (alcoholysis), glycols (glycolysis), amines (aminolysis) and ammonium (ammoniolysis) [3-4]. As a result, different substances and/or products with added value for the chemical industry can be obtained.
Glycolisis, a type of alcoholysis, is the most suitable for the development of unsaturated polyester, vinylester, epoxy, alkyl resin and polyurethanes. This reaction consists in the breaking of ester bonds by glycols, producing olygomers or olygoesters diol/polyol with terminal hydroxyl groups. The olygoesters coming from PET glycolysis are “renewable” chemical reactives for the production of resins previously mentioned.
Substances and products obtained are recycled materials, from the environmental point of view (contributing to sustainable development and providing eco-innovated products), although from technical point of view they have same properties than initial materials, in contrast to traditional mechanical recycling in which a decreasing in properties could be observed in different degrees.
These factors have recently promoted the growing interest in the options to use PET wastes for the production of products as unsaturated polyester resins, alkyl resin, polyurethane foams and polymer concrete. In this context, RESIPET project “Development of New Thermosetting Resins from Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Waste” is being developed by BARPIMO Company and AIMPLAS- Plastics Technology Centre.
2 Development
2.1 Introduction
The main goal of RESIPET Project is the industrial development of thermoset resins (alkyl resins and unsaturated polyester), through raw materials coming from chemical recycling of multilayer or color wastes from Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) at a competitive cost and low environmental impact.
Project benefits and the developed products are relevant as follows:
- Reduction of environmental impact of alkyl and unsaturated polyester resins (less carbon footprint).
- Replace this kind of waste PET removal with material recycling (chemical recycling), following waste hierarchy and obtaining an environmental improvement.
- Competitive cost of new developed resin (lower than conventional thermoset resins).
- Use of separable layers of multilayer packaging. Recycling of polypropylene or polyethylene from this packaging.
The project structure is divided in four steps as it is detailed as figure 2: i) selection and characterization of PET wastes, ii) preparation of PET waste, iii) chemical reaction, iv) resin production
2.2 Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) waste selection and preparation
Search and selection of PET waste was carried out taking into account the following characteristics:
- They are currently not recycled (they can be a problem for PET recyclers).
- Good accessibility, according to: a critical volume, homogeneous, competitive price
Taking these premises into account, the following waste has been evaluated from different sources:
- Fresh pizza packaging waste
- Frozen pizza packaging waste
- Slurry packaging waste
- 1) b)
2.3 Chemical recycling and resin production
PET wastes selected and conditioned have been subjected to the chemical recycling process according to scheme detailed in figure 4, obtaining a new poliol (OligoPET). These will be the starting recycled reagents for the synthesis of alkyd resins and enamels, as well as for the production of unsaturated polyester resins.
The virgin and recycled unsaturated polyester obtained by glycolysis have been characterized by different tests: viscosity, gel time, Persoz hardness, density, non-volatile content, acid number …
| Table 1. Characterization of virgin and recycled unsaturated polyester resins | ||
| Resin | Virgin | Recycled |
| Viscositty | 320 cps | 345 cps |
| Gel time | 7 minutes | 8 minutes |
| Persoz Hardness | 240 | 262 |
| Density | 1.14 g/ml | 1.14 g/ml |
| Nonvolatile content | 65.38 % | 66.16 % |
| Acid index (mg KOH/g resin) | 19.65 | 18.48 |
3 Results
Results of the project are detailed as follows:
- A new poliol (OligoPET), from chemical recycling of PET waste
- Unsaturated polyester resin formulated by the replacement of some of polyacids and polyols by the new OligoPET.
- Alkyl resin has been formulated with the same principle.
- The results of the characterization carried out show similar results to the unsaturated polyester resin from the PET wastes and to a standard resin:
Figure 5 shows an approach of the project and its involvements and results in terms of products and economic viability of the process.
4 Conclusions
As conclusions, it can be established that:
- The implementation of technologies of preparation and chemical recycling of PET wastes coming from multilayer or color packaging are feasible.
- Alkyl and unsaturated polyester resins from not valued PET wastes (multilayer or colour packaging) can be obtained by chemical recycling.
- Thermoset resins with low environmental impact and at competitive cost can be developed
Acknowledgments
This work has been co-funded by Competitivity and Economy Ministry in “Retos-Colaboracion” National Program of Research, Development and Innovation oriented to Societal Challenges RTC-2015-3855-5 and FEDER Funds.
Referencias
[1] Directiva 94/62/CE del Parlamento Europeo y del Consejo, de 20 de diciembre de 1994, relativa a los envases y sus residuos. DO L 365 de 31.12.1994
2 Mohamadi, M. et al. “Synthese und Charakterisierung von BHETA basierten neuen Polyurethanen”. Mat-WissU Werkstofftech, 41 (8):682-88 (2010)
3 Spychaj T. “Chemical Recycling of PET: Methods and Products”. En: FAKIROV S. “Handbook of Thermoplastic Polyesters: Homopolymers, Copolymers, Blends, and Composites”. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, FRG. doi: 10.1002/3527601961.ch27, 2005: 1252-1290
4 Shamsi R. et al. “Synthesis and characterization of novel polyurethanes based on aminolysis of poly(ethylene terephthalate) wastes, and evaluation of their thermal and mechanical properties”. Polym Int 58:22–30 (2009)
Document information
Published on 15/07/18
Accepted on 15/07/18
Submitted on 15/07/18
Volume 02 - Comunicaciones Matcomp17 (2018), Issue Núm. 3 - Reciclaje y Sostenibilidad y Procesos de Fabricación I, 2018
DOI: 10.23967/r.matcomp.2018.07.007
Licence: Other
Share this document
Keywords
claim authorship
Are you one of the authors of this document?